Your GFR tells how much kidney function you have. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney.

It may be estimated from your blood level of creatinine.
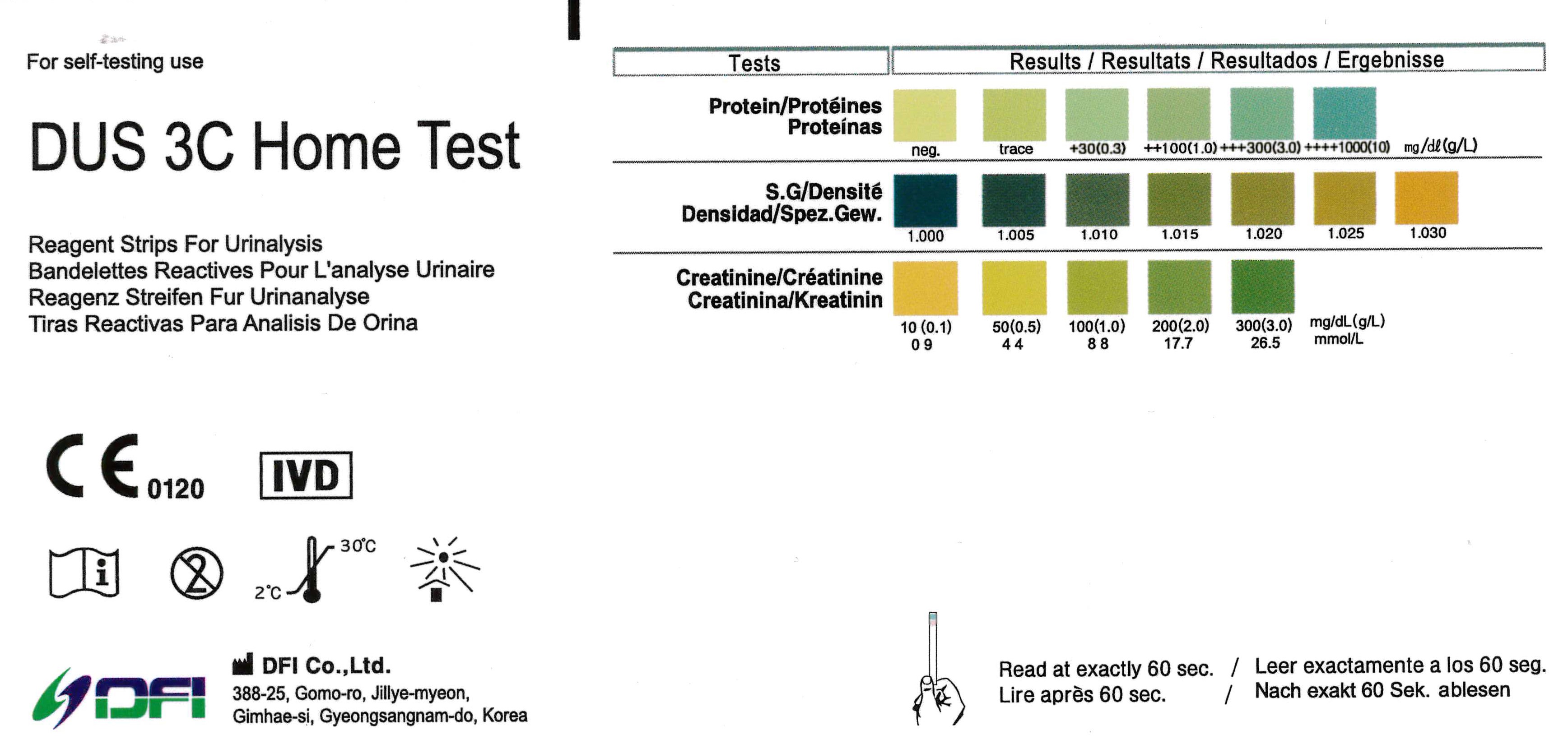
Kidney test results. How the tests are performed Kidney function tests usually require a 24-hour urine sample and a. The results of the test mean the following. Complete blood count CBC.
Three positive results over three months or more is a sign of kidney disease. Blood Test to estimate your GFR. The creatinine clearance test involves urine collection over a 24 hour period and can also provide an estimate of your kidney function.
You collect all your urine for 24 hours and then have a blood test done. There is a 2000 administrative fee and. Interisland Pre-Travel Trusted Testing Partner.
Blood Tests For Kidney Problems Blood tests for kidney problems are quite common and are done. Understanding test results Monitoring kidney function. The GFR Glomerular Filtration Rate test result determines how well the toxins or waste materials are being filtered by the kidneys.
Glomerular Filtration Rate GFR. The GFR blood test measures the creatinine level with respect to the persons age gender weight height and race. In males normal levels may vary slightly between labs.
Kidney or bladder infections kidney disease kidney stones diabetes. Ask your health care provider when your GFR should be checked again. Blood and urine tests show how well.
You will be notified with your lab results on the same day and information on next steps if your lab results are positive. The test also measures the level of certain salts such as potassium chloride sodium and bicarbonate. If your GFR falls below 30 you will need to see a kidney disease specialist called a nephrologist.
These tests are generally used to gauge how well your kidneys are working. If your urine test comes back positive for protein the test should be repeated to confirm the results. Labeled Cross Section of a Human Kidney.
Normal creatinine clearance for healthy women is 88-128 mLmin. The creatinine levels in both urine and blood are determined and compared. Any result lower than 60 millilitersminute173m 2 may be a warning sign of kidney disease.
The creatinine clearance test requires a urine sample as well as a blood sample. Checking the effectiveness of. This is a test that measures the number of different cells in the blood.
Your blood will be tested for a waste product called creatinine. 13 rows Healthy kidneys remove wastes and excess fluid from the blood. A GFR of 60 or more is in the normal range.
Your doctor should use the results of your serum creatinine test to calculate your GFR. Some minerals in the blood need to be closely monitored because normal levels can often change in. Your Kidney Test Results Author.
If the test comes back positive for one or more of these particles it may indicate an underlying issue such as. If you are cancelling your testing fill out the refund form and we will contact you if additional information is required. This test result is often abnormal in people with kidney cancer.
The kidney blood test results tell us the level of urea and creatinine present. The kidney ACR and GFR values are considered to be of great importance. And 97 to 137 mLmin.
Anemia having too few red blood cells is. Blood urea nitrogen BUN level is another indicator of kidney function.