There is a mild decrease in kidney function. Research shows that people with kidney disease who become malnourished have low serum albumin levels and do not get enough protein may suffer from complications.
How this test is conducted.

Kidney disease lab values. They can also screen for monitor or diagnose kidney disease. A GFR below 15 indicates that you need to start a treatment for kidney failure. The normal serum creatinine range is 0611 mgdL in women and 0713 mgdL in men.
Stage 5 kidney disease or end stage renal disease ESRD occurs when your estimated glomerular filtration rate eGFR falls below 15 indicating that your kidneys are failing or close to failing. Everything you need to know. Electrolytes specifically potassium sodium chloride and carbon dioxide CO2 Urea urea nitrogen or blood urea nitrogen BUN.
This is considered kidney disease. The difference shows how well your kidneys work. A GFR of less than 60 may mean you have kidney disease.
Moderate decrease in kidney function. A GFR of 15 or lower may mean kidney failure. An optimal eGFR is higher than 90 while stage 5 CKD presents itself in an eGFR of less than 15.
It may be estimated from your blood level of creatinine. Microalbuminuria or albumin-to-creatine ratio tests. The normal value for GFR is 90 or above.
A GFR below 60 is a sign that the kidneys are not working properly. Urinalysis is a broad urine test that helps doctors identify underlying issues or determine which test to use next. Most people below this level need dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Treatment such as dialysis or a kidney transplant is necessary to sustain life. A GFR below 60 may mean kidney disease. If your GFR falls below 30 you will need to see a kidney disease specialist called a nephrologist.
There may be slight kidney damage. The normal serum albumin in a healthy adult is 35 gdl. A blood sample is taken and sent for analysis.
Urinalysis may help. So the higher your eGFR the better your estimated kidney function. A normal serum albumin is a measure of good nutrition.
A GFR of 60 or higher is in the normal range. Kidney failure and need for dialysis or transplant eGFR less than 15. Kidney function tests.
Normal GFR can vary according to age as you get older it can decrease. Once the GFR decreases below 15 one is at high risk for needing treatment for kidney failure such as dialysis or a kidney transplant. 7 to 20 milligrams per deciliter mgdl.
If your GFR falls below 30 you will need to see a kidney disease specialist called a nephrologist Your kidney doctor will speak to you about treatments for kidney failure like dialysis or kidney transplant. Talk with your health care provider about how to keep your kidney health at this level. In the diagnostic stage the early and later stages of CKD including ESRD to measure effectiveness of treatment.
In renal failure patients predialysis levels may be seen as high as 20 mgdl. Your GFR tells how much kidney function you have. GFR is l5 or less.
Glomerular Filtration Rate GFR. A GFR of 15 or less is called kidney failure. If two or more levels are high you may have kidney disease.
This is usually not considered an emergency situation although normal range is 06 mgdl to 13 mgdl but would indicate the need for dialysis to lower the value. A GFR below 15 indicates that you need to start one of these treatments. There is severe decrease in kidney function.
The test panels vary by laboratory but generally include. 6 rows Below are the common chronic kidney disease lab tests performed to assess kidney function. This test compares creatinine in your blood and urine.
BUN is the nitrogenous end product of protein metabolism. The target for adults with CKD is 4 gdl. Blood Urea Nitrogen BUN.
 Dialysis Clinic Inc Prolonging Function
Dialysis Clinic Inc Prolonging Function
 Exploring Chronic Kidney Disease Ems World
Exploring Chronic Kidney Disease Ems World
 Neutrophil Lymphocyte Ratio In Aute Renal Failure
Neutrophil Lymphocyte Ratio In Aute Renal Failure
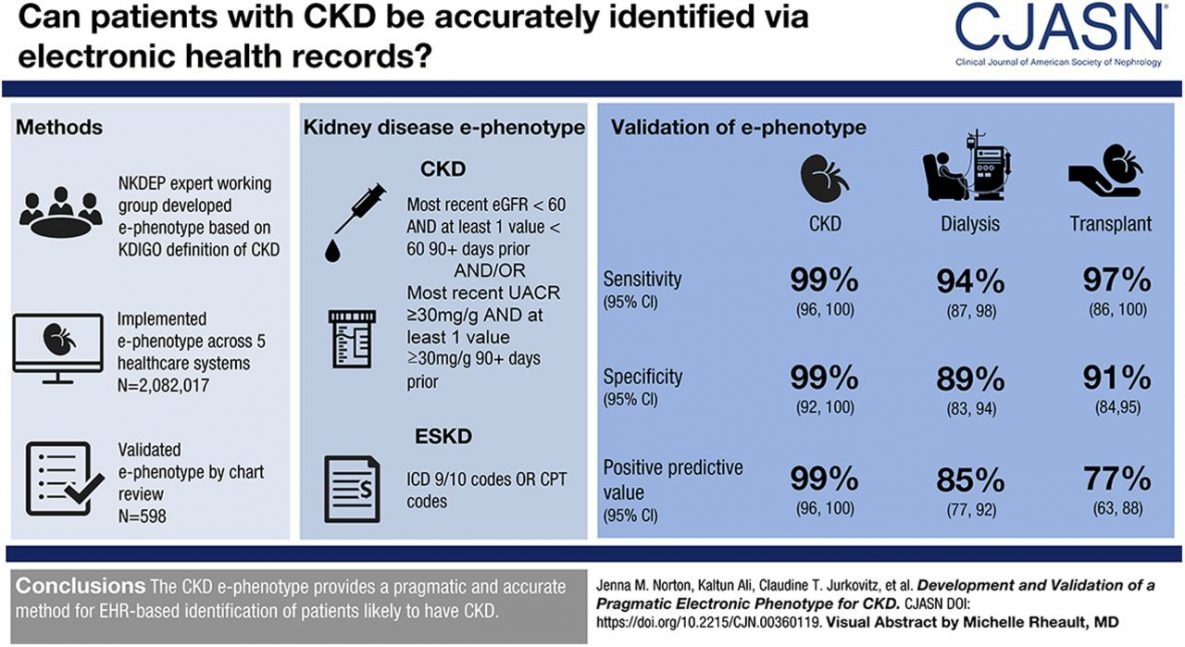 Using Electronic Health Records To Identify Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease Cdc
Using Electronic Health Records To Identify Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease Cdc
 Comparison Of Laboratory Values Before And During Acute Renal Failure Download Table
Comparison Of Laboratory Values Before And During Acute Renal Failure Download Table
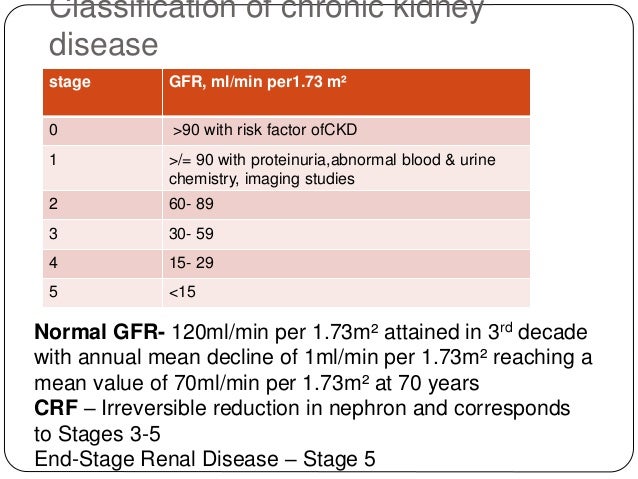 Approach To Laboraratory Diagnosis Of Acute And Chronic Renal Failure
Approach To Laboraratory Diagnosis Of Acute And Chronic Renal Failure
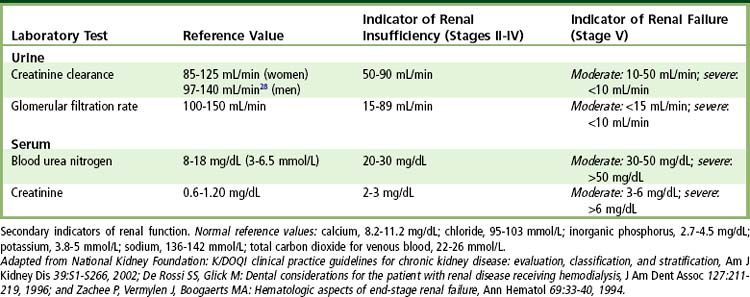 12 Chronic Kidney Disease And Dialysis Pocket Dentistry
12 Chronic Kidney Disease And Dialysis Pocket Dentistry
Demystifying Chronic Kidney Disease Clinical Caveats For The Family Physician British Columbia Medical Journal
 Chronic Kidney Disease Detection And Evaluation American Family Physician
Chronic Kidney Disease Detection And Evaluation American Family Physician
 Clinical And Laboratory Values For All 35 Non Diabetic Renal Disease Download Table
Clinical And Laboratory Values For All 35 Non Diabetic Renal Disease Download Table
 Lab Values Of The Renal Failure Patient On Advance For Nurses Lab Values Renal Failure Kidney Failure Treatment
Lab Values Of The Renal Failure Patient On Advance For Nurses Lab Values Renal Failure Kidney Failure Treatment
 Renal Failure In Patients With Multiple Myeloma Almueilo Sh Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl
Renal Failure In Patients With Multiple Myeloma Almueilo Sh Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl


No comments:
Post a Comment