Causes of Acute Kidney Injury Based on Laboratory Findings Staging Criteria for Acute Kidney Injury KDIGO 2012 Overview of Intrarenal Acute Kidney Injury Acute kidney injury is a rapid decrease in renal function over days to weeks causing an accumulation of nitrogenous products in the blood azotemia with or without reduction in amount of. Acute kidney injury AKI also known as acute renal failure ARF is a sudden episode of kidney failure or kidney damage that happens within a few hours or a few days.
 Recent Knowledge On The Pathophysiology Of Septic Acute Kidney Injury A Narrative Review Sciencedirect
Recent Knowledge On The Pathophysiology Of Septic Acute Kidney Injury A Narrative Review Sciencedirect
Changing concepts in the disease pathogenesis and approaches to treatment based on.
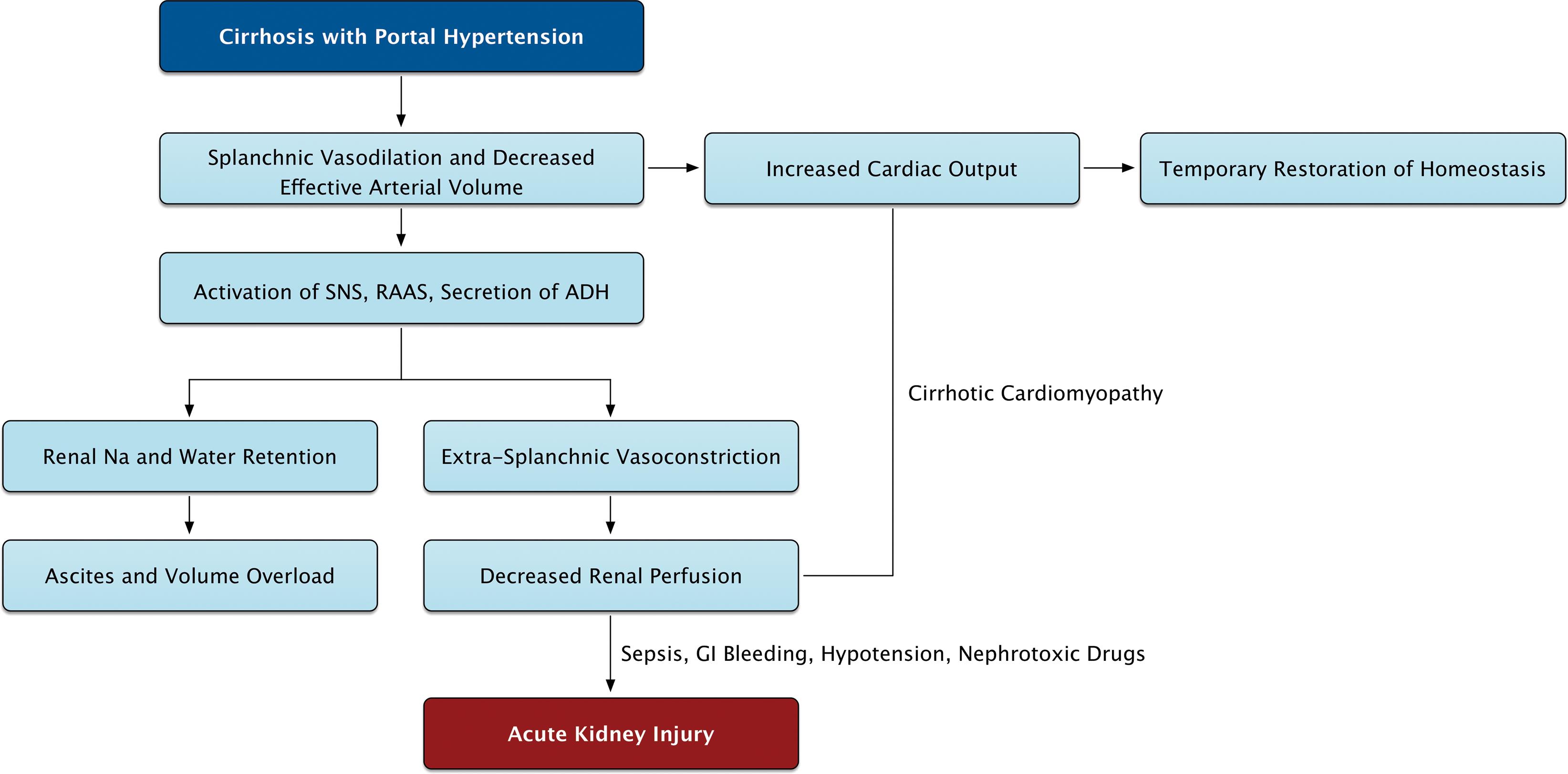
Acute kidney injury pathophysiology. These conditions cause urine to flow back to the kidneys causing damage. The causes of acute kidney injury are divided up into 3 main categories. Other glomerular pathology associated with COVID-19 might be coincidental or a second hit phenomenon.
The variability in the occurrence of AKI has been attributed to the difference in geographic locations raceethnicity and severity of illness. Acute kidney injury happens when the kidneys are suddenly damaged by things like certain medications sepsis or a lack of blood flow. Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney Injury.
There is a decreased glomerular filtration rate. Acute kidney injury AKI as a consequence of ischemia is a common clinical event leading to unacceptably high morbidity and mortality development of chronic kidney disease CKD and transition. High levels of nitrogenous compounds urea and creatinine in the blood due to insufficient filtering in the kidneys.
The most common cause of kidney injury in patients with COVID-19 is acute tubular injury. Acute Kidney Injury AKI is the term that has recently replaced the term ARF. Collapsing glomerulopathy is a recognized glomerular pathology associated with COVID-19 that most commonly affects individuals with high-risk APOL1 polymorphisms.
AKIs include prerenal intrarenal and postrenal causes. Acute kidney injury is characterized by a rapid decrease in renal functioning with an increased accumulation of waste products such as urea and creatinine in the blood. Prerenal causes of AKI lead to reduced blood flow in the kidneys.
Severe kidney dysfunction within a few hours or days results in a significant decrease oliguria or complete elimination of urine anuria with electrolyte imbalance often requiring hemodialysis. Acute kidney injury AKI most commonly occurs in the hospital setting and hospital-acquired AKI accounts for 22 of all AKI cases worldwide. This chapter focuses on the pathophysiological principles of Acute Kidney Injury AKI with special emphasis on the structural cellular and molecular alterations occurring in ischemic nephrotoxic and septic AKI.
As a result the kidneys are not able to perform their function due to the lack of oxygen supply. It is also believed to be due to ferrihemate which is. Acute kidney injury AKI previously called acute renal failure ARF is a condition of sudden kidney failure in patients with or without preexisting chronic kidney disease CKD.
AKI causes a build-up of waste products in your blood and makes it hard for your kidneys to. Acute kidney injury AKI is common among hospitalized patients with Coronavirus Infectious Disease 2019 COVID-19 with the occurrence of AKI ranging from 05 to 80. Acute kidney injury AKI most commonly occurs.
AKI is defined as an abrupt within hours decrease in kidney function which encompasses. Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney Injury. Postrenal conditions lead to the obstruction of urine flow.
Acute kidney injury AKI previously called acute renal failure ARF is a sudden decrease in kidney function that develops within 7 days as shown by an increase in. AKI causes 2 million deaths per year and 50 of critically ill patients develop AKI. AKI is believed to be due to decreased extracellular volume which results in renal vasoconstriction.
This damage can be reversible as long as it is treated promptly.
