An atrial septal defect ASD is an abnormal hole in this wall. ASD is a heart problem that is present at birth congenital.
 Atrial Septal Defect Wikipedia
Atrial Septal Defect Wikipedia
When this wall does not form correctly it can result in a defect that remains after birth.
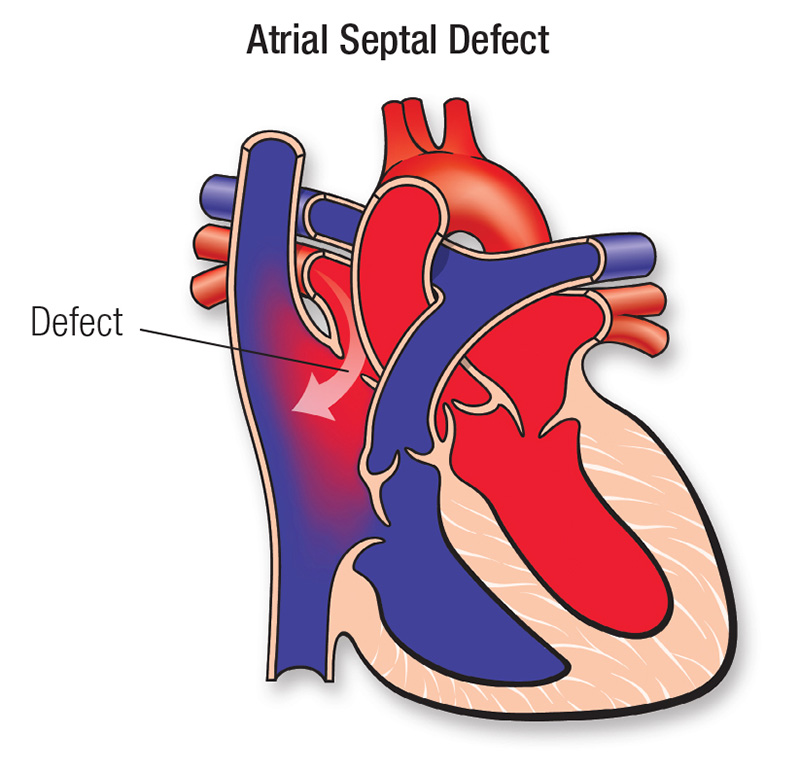
Atrial septal defect asd. This allows red blood to pass through into the right side of the heart leading to enlargement of the right ventricle and excessive flow in the lung circulation. What Is an Atrial Septal Defect. An atrial septal defect ASD is a hole in the septum which is the muscular wall that separates the hearts two upper chambers atria.
Arrhythmias atrial fibrillation supraventricular tachycardias Pulmonary HTN RV dysfunction shunt reversal R L with hypoxemia Tricuspid valve pulmonic valve disease perioperative risk of. Atrial Septal Defect ASD Considerations. High defects of the atrial wall sinus venosus ASD This type of ASD is commonly seen together with an abnormal position of the right upper pulmonary vein one of the blood vessels bringing oxygenated blood back to the heart.
Atrial septal defect ASD is one of the more commonly recognized congenital cardiac anomalies presenting in adulthood. Atrial septal defect ASD This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital explains the. Children are rarely symptomatic but long-term complications after age 20 years include pulmonary hypertension heart failure and atrial arrhythmias.
An Atrial Septal Defect ASD is a hole in the atrial septum or muscle wall that separates the upper chambers of the heart the right and left atria singular atrium. An atrial septal defect ASD sometimes called a hole in the heart is a type of congenital heart defect in which there is an abnormal opening in the dividing wall between the upper filling chambers of the heart the atria. Size shunt L R R L Complications of chronic L to R shunt.
In essence the problem is that the body is getting less volume of the oxygenated blood. Atrial septal defects are one of the most common heart defects seen. An ASD is a defect where blood abnormally flows from one atrium to the other atrium andor unanticipated vessels.
This hole allows oxygen-rich blood from the left atrium to flow into the right atrium instead of flowing into the left ventricle as it should. The commonest form of this defect so called Secundum ASD is a defect in the central part of the Atrial Septum the partition separating the Atriums. ASD is characterized by a defect in.
This left to right shunt sends oxygenated blood to the right side of the heart. Atrial septal defect ASD is a heart defect that is present at birth congenital. Because of the lower pressure in the right atrium this hole typically allows oxygenated blood from the lungs to move or shunt from the left into the right atrium.
When an atrial septal defect is present blood flows through the hole primarily from the left atrium to the right atrium. An atrial septal defect ASD is a hole in the part of the septum that separates the atria the upper chambers of the heart. ASDs can happen on their own.
Click here for Patient Education An atrial septal defect ASD is an opening in the interatrial septum causing a left-to-right shunt and volume overload of the right atrium and right ventricle. As a baby develops in the womb a wall septum forms that divides the upper chamber into a left and right atrium. What is an atrial septal defect ASD.
An atrial septal defect ASD is a hole in that septum. This shunting increases the blood volume in the right atrium which means more blood flows through. The atrial septum is the wall between the 2 upper chambers of the heart right and left atria.
An ASD is a defect you are born with congenital defect that happens when the septum does not form properly. Etiology severity of ASD.
