Infants with transposition of the great arteries TGA are usually born at term with cyanosis apparent within hours of birth. In a normal heart there are two large arteries that carry blood out of the heart.
 Cardiology Transposition Of The Great Arteries
Cardiology Transposition Of The Great Arteries
D-Transposition of the great vessels d-TGA is a congenital heart defect where the aorta and pulmonary artery are switched from their normal positions.

Transportation of the great vessels. The aorta carries blood from the left ventricle to the vessels of the rest of the body. The great arteries in this anomaly refer to the aorta and the pulmonary artery the two major arteries carrying blood away from the heart. Ordinarily blood returning to the heart is depleted in oxygen.
Transportation of the great vessels. There are two great arteries that transport blood away from the heart the pulmonary artery and the aorta. In cases of transposition of the great arteries these vessels arise from the wrong ventricle.
The pulmonary artery is joined to the left pumping chamber ventricle and the. Report of a case. Until aroud 1980 this delicate surgery could not be performed safely and an alternative procedure was used redirecting blood within the atriums.
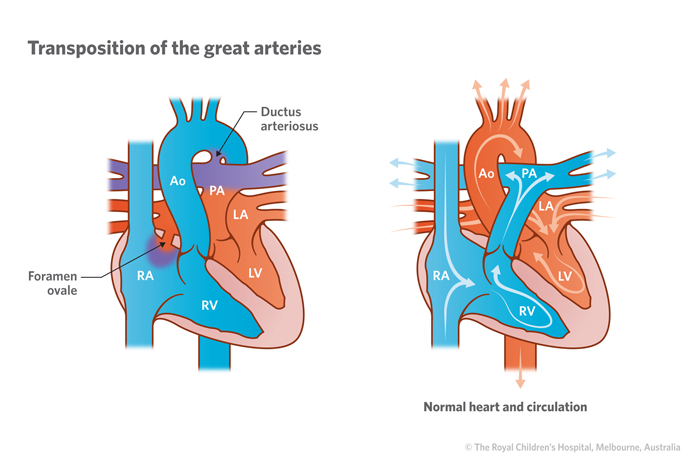
The clinical course and manifestations depend on the extent of. Also called transposition of the great vessels TGA or TGV No communication exists between the right and left side of the heart Each side of the heart has its own circulation and its the opposite of how circulation should occur in a normal heart. In the normal heart the right ventricle pumps out to the pulmonary artery to the lungs and the left ventricle pumps out to the aorta to the body.
It accounts for up to 7 of all congenital cardiac anomalies 1 and can be assessed with echocardiography gated cardiac CT or cardiac MRI. This was called a Senning operation. The two major arteries that carry blood away from the heart -- the aorta and the pulmonary artery -- are switched transposed.
Transposition of the great arteries is a condition where that the two main blood vessels leaving the heart the pulmonary artery which takes blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen and the aorta which takes blood from the heart to the body are swapped over switched. What is D-Transposition of the Great Vessels. The small coronary arteries which feed the heart muscle with blood need to be transferred as well as the two Great Arteries Aorta and Pulmonary Artery.
The aorta is attached to the right-sided pumping chamber ventricle instead of the left. Transposition of the Great Arteries. Handbook of Pediatric Dentistry Fourth Edition 2013.
Normally the pulmonary artery carries blood from the right ventricle to the lungs. Transposition of the great arteries TGA is a group of congenital defects in which the position of major blood vessels of the heart are switched. Transposition of the great arteries TGA also known as transposition of the great vessels TGV is the most common cyanotic congenital cardiac anomal y presenting during the newborn period with cyanosis in the first 24 hours of life.
Transposition of the great arteries. Sachdev Y Subramanian AR. Transposition of the Great Vessels Transposition of great vessels when the aorta exits the heart from the right side and the pulmonary artery exits from the left.
They are transposed from their normal position so that the aorta arises. Transposition of the great arteries TGA is a complex congenital heart defect. In rare cases even the chambers of the heart will be swapped.
Normally the aorta leaves the left ventricle carrying oxygen-rich red blood to the body and the pulmonary artery leaves the right ventricle carrying oxygen-poor blue blood to the lungs to get oxygen. In children with TGA these arteries are connected to the heart abnormally. Consequently the aorta arises from the right ventricle and the pulmonary trunk arises from the left ventricle thus creating two parallel circuits incompatible with life.
Initial treatment of transposition of the great arteries consists of maintaining ductal patency with continuous intravenous IV prostaglandin E 1 PgE 1. Transposition of the great arteries TGA is a heart defect that occurs from birth congenital. Transposition of the great arteries TGA is a congenital pediatric cardiac defect arising from an embryological discordance between the aorta and pulmonary trunk.
TGA causes the diversion of normal blood circulation robbing the body of oxygen and nutrients. Transposition of the great arteries TGA is a rare but serious congenital present at birth heart defect in which the two main arteries leaving the heart are reversed transposed.
